
In most cases, this results in one or perhaps a few stings. Generally, insects such as bees and wasps aren't aggressive and only sting in self-defense. Talk to your doctor or an allergy specialist about prevention measures such as immunotherapy ("allergy shots") to avoid a similar reaction in case you get stung again. People who have a severe allergic reaction to a bee sting have a 25% to 65% chance of anaphylaxis the next time they're stung.
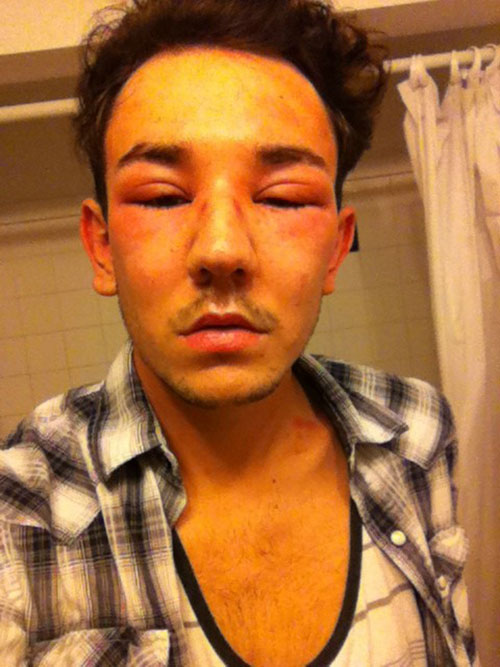
#Bee sting on face skin
Skin reactions, including hives and itching and flushed or pale skin.Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include: A small percentage of people who are stung by a bee or other insect quickly develop anaphylaxis. Severe allergic reactionĪ severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to bee stings is potentially life-threatening and requires emergency treatment. If this happens to you, talk to your doctor about treatment and prevention, especially if the reaction becomes more severe each time. But some people develop similar moderate reactions each time they're stung. Having a moderate reaction doesn't mean you'll have a severe allergic reaction the next time you're stung. Moderate reactions tend to resolve over five to 10 days. Swelling at the site of the sting that gradually enlarges over the next day or two.Some people who get stung by a bee or other insect have a bit stronger reaction, with signs and symptoms such as: In most people, the swelling and pain go away within a few hours. Instant, sharp burning pain at the sting site.Most of the time, bee sting symptoms are minor and include: Having one type of reaction doesn't mean you'll always have the same reaction every time you're stung or that the next reaction will necessarily be more severe. Bee stings can produce different reactions, ranging from temporary pain and discomfort to a severe allergic reaction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
